What is SaMD (Software as a Medical Device) and how is it regulated?
Building a SaMD (Software as a Medical Device) is, to say the least, a challenge. To start things off, let’s take a step back and define exactly when a medical device is considered to be a SaMD, and when it’s not.
Defining SaMD (Software as a Medical Device)
Before looking into building a SaMD, you must be 100% certain that the type of medical device you will be, or are currently building is, in fact, a SaMD. The IMDRF (International Medical Device Regulators Forum), an international group of regulators that aim to harmonise regulatory requirements for medical products, including SaMDs, provide us with a clear definition of what a SaMD exactly is:
The term “Software as a Medical Device” (SaMD) is defined as software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes that perform these purposes without being part of a hardware medical device.
Basically, there are 2 main types of medical device software. The figure below the terms explains the process of making the distinction between both of them in a more visual way.
1. Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)
In this case, the software in itself serves as a medical product.
2. Software in a Medical Device (SiMD)
In this case, the software in itself serves as a medical product.
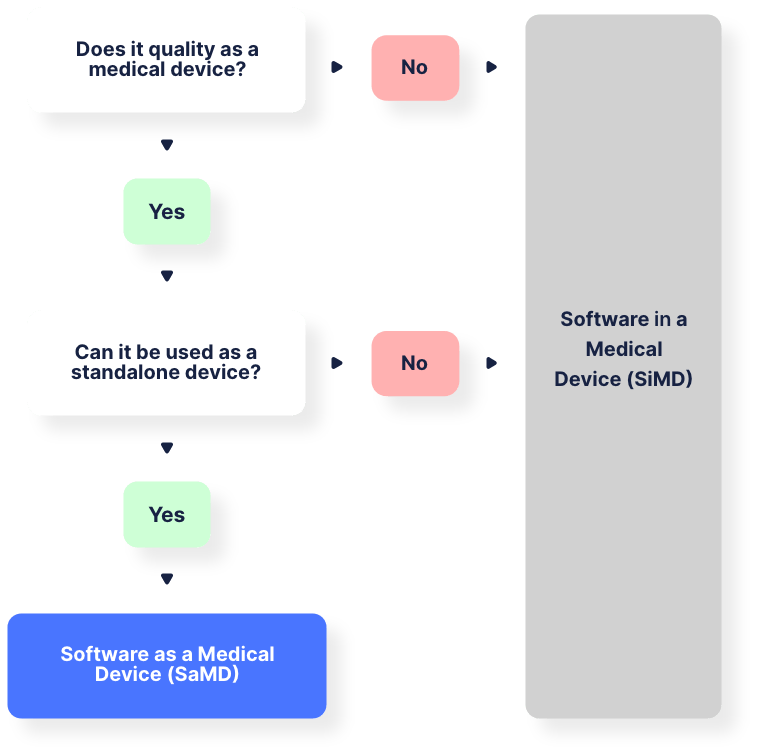
Next to these 2 primary groups, there are also other types of medical device software. For example, an accessory product to medical devices is one, but we will not be diving further into these types of software.
The many types of SaMD solutions
The digital health landscape is enormous. Therefore, there are numerous types of SaMD solutions already available, and many, many more are on the way. Most SaMDs are related to some kind of diagnosis, prevention, treatment, prediction, alleviation or monitoring in the context of an illness, injury or disability. In addition, if the medical device, running as standalone software, is involved in the control of conception or IVD & sterilisation, it is also a SaMD. SaMDs can range from software that can detect cancer based on smartphone images, to a sleep app that analyses the data to form the basis of a sleep treatment plan.

It’s quite impossible to create a complete list of all types of SaMDs, because as seen in the figure above, the digital landscape is vast. An easy trick to know whether or not medical device software can be seen as SaMD is whether or not the software is run on non-medical devices like smartphones, smartwatches, tablets and so on.
The key benefits of SaMD solutions
There are two key benefits of SaMD solutions that we’d like to share:
1) The use of data to improve health in patients
SaMD solutions make it possible to collect data much more easily and faster than some of the traditional health improvement methods. Also, as these kinds of solutions are highly regulated, the quality of the data is often very high as well. As a result, SaMDs enable the health space to create patient-centred solutions that are capable of improving patient health tremendously.
2) The use of the software is much more versatile than hardware-based solutions
SaMDs exist mostly in the cloud. This is a big win in terms of speed and versatility, not only when building these kinds of solutions, but also the updates and adaptations to said SaMD solutions. By utilising the latest technologies, connected medical devices are much easier to create, build and keep in the air, in contrast to the traditional hardware-based health improvement solutions.

A real-life example of a SaMD
For us, it’s quite easy to give you a very tangible example of a SaMD. Our customer
FibriCheck has created a pure form of SaMD. FibriCheck is an app that you can download directly from the app store or the play store, that enables you to accurately detect Atrial Fibrillation (irregularities in your heart rhythm) using only the app, your smartphone, your smartphone camera and your index finger.

What are the key elements of SaMD?
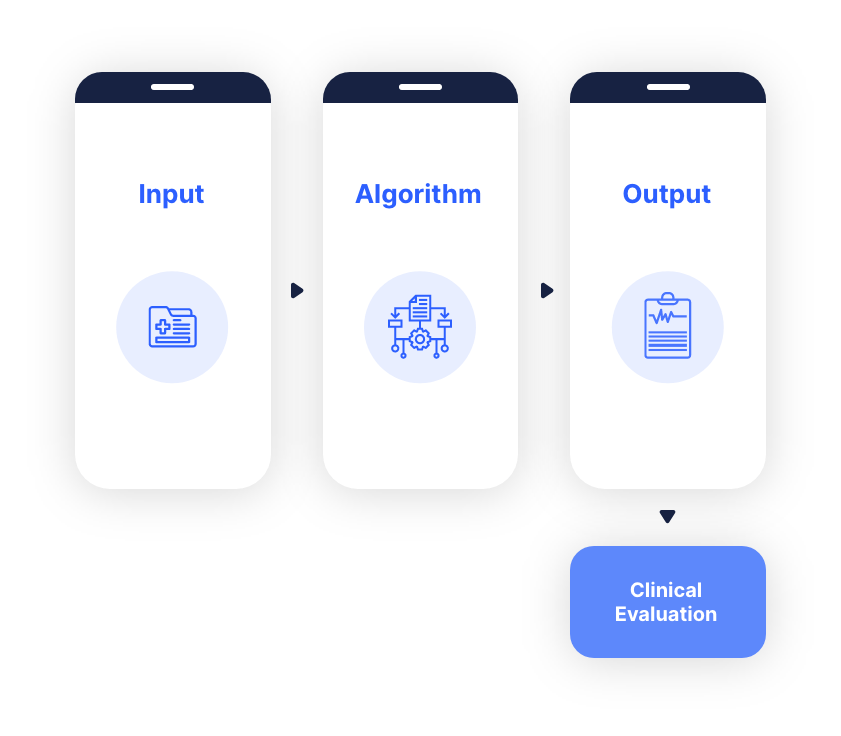
There are 4 basic elements that you will encounter in almost every type of SaMD solution:
1. SaMD inputs
These are the inputs required in order for the SaMD to work correctly. This can range from patient data to lab results, image data, physiological states, symptoms and so on.
2. SaMD algorithm
At the core of the SaMD, the algorithm is the key player. The algorithm holds, in most cases, the IP of the solution. Here you will find the set of instructions and logic, required for the SaMD to accomplish its task of generating some kind of medical related output.
3. SaMD outputs
After the inputs are entered into the SaMD, and the algorithm goes to work with them, some kind of output will be generated. These outputs will inform, drive, diagnose or treat the user of the SaMD.
4. Clinical Evaluation
The outputs of the SaMD will be subject to clinical evaluation, which is a very challenging and difficult phase for every SaMD to go through. We have written an in-depth blog post on how to get through this stage with flying colours if you feel you need more information on this phase.
How are SaMD solutions categorised?
When diving into the categorisation of SaMD solutions, it’s important to know that, although similar, the approach is different in the EU and the US regulated markets.
EU SaMD (or MDSW) categorisation
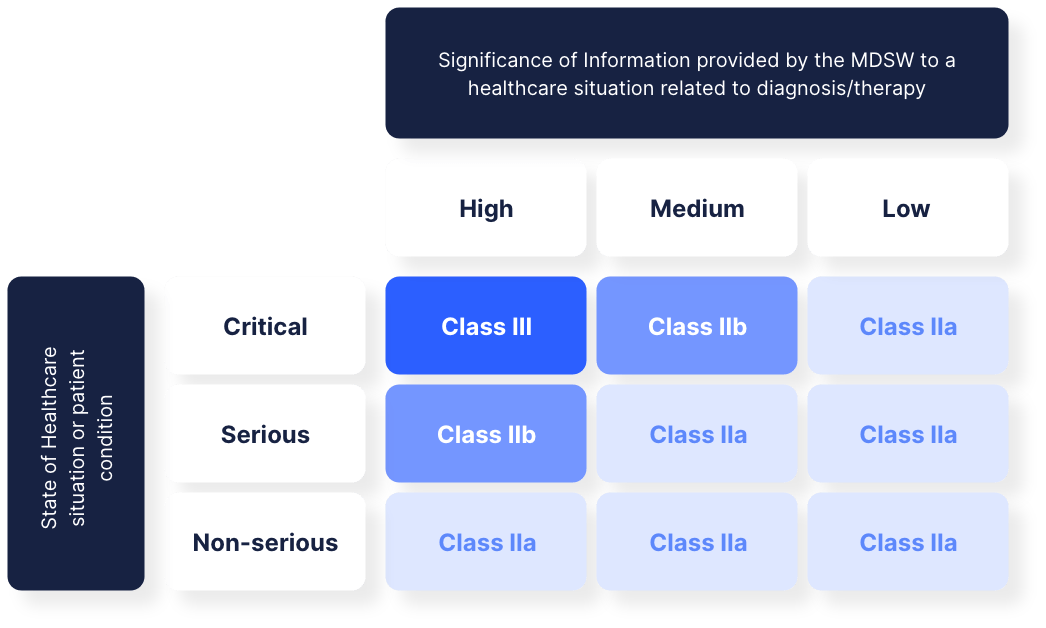
To start things off, it’s important to note that although we talk about SaMD solutions, this term is not used in the EU officially. In the EU, the term “Medical Device Software” or “MDSW” is used. In the EU, the MDR defines 4 different classes; being classes I, IIa, IIb and III. These classes align to a rather large extent with the
classification created by the IMDRF as well. In line with the EU classification of other medical devices, these classes depend on the intended purpose of the medical device, and the risks it might create. In the figure below, you can see the overview of classes used by the MDR.
If we dive a bit deeper into the risk aspect, it’s also important to note that the EU MDR uses the harmonised ISO 62304 standard to assess risk. If you plan on launching a SaMD in the EU, you will need to get a certificate of conformance from a notified test body for this standard.
US SaMD categorisation
In the US, it’s the FDA that establishes the different classes for SaMD solutions. Here, classification is based on both impact and functionality controls that are needed in order to prove safety and effectiveness. There are 3 categories that a SaMD can fall into according to the FDA: Class I, Class II and Class III.
What is important to note, is that the FDA also approaches risk classification based on the ISO 62304 standard, be it with some different terminology here and there.
What is the major international regulatory framework for SaMD (Software as a Medical Device) solutions?
In this section, we will dive a bit deeper into the regulatory landscape surrounding SaMD solutions. Especially in medical device development, the regulatory requirements can be quite challenging. Looking at the regulatory burdens early in the development process of a SaMD is the key to successfully launching the SaMD later on.
SaMD regulations: EU MDR vs FDA
First off, it is important to note that there is a difference when you are launching a SaMD into the EU or US markets. There is a clear distinction between the two markets, be it the way they are regulated. On the one hand, the EU market is regulated by the MDR (Medical Device Regulation), while on the other, the US market is regulated by the FDA (Food & Drugs Association). You might also have heard of the MDD (Medical Device Derivative), which has been replaced in the EU by the MDR.
Luckily, with the coming of the MDR, both types of regulations are much more aligned than they were before, especially in the case of the QMS (Quality Management System) requirements. More specifically, the ISO 13485 standard, but more on that later on.
Also, the IMDRF standards for SaMD are a harmonising effort, as both the EU and the FDA chair the council of the international forum. Although much more harmonised than before, it’s still very important that you deep-dive into the similarities and differences between the two if you plan on entering both markets.
SaMD quality management systems and standards: ISO 13485 vs FDA QSR
When we are talking about quality management for a SaMD, we are mostly talking about the ISO 13485 standard. The ISO 13485 standard is an international one that is required in order to launch a SaMD in the EU, Canada, Australia and many other markets. If you plan on getting a CE Mark for selling your SaMD in the EU, you will need to become compliant with the MDR, and to be compliant with the MDR, you will need to be compliant with the ISO 13485 standard. As you can see, it’s quite a big chunk of regulatory work to become a regulatory compliant SaMD manufacturer.
The US has its own set of regulations for SaMD companies. In particular, US regulation 21 CFR Part 820, also known as the US FDA QSR, is the one that has been implemented for over 20 years.
Complying with both types of regulations is a cost and time-consuming effort for many international SaMD providers. Luckily, the FDA is currently in the process of adapting the ISO 13485 requirement as well, which would make it much easier for companies to sell internationally. Only a few additional stipulations would be added to the FDA version, as both of them already are quite similar. This is also a result of the harmonisation effort of the IMDRF.
SaMD data protection: GDPR vs HIPAA
Software as a Medical Device will always rely on patient data in order to work properly and have its desired outcome. And with patient data, comes data protection and data security. Both the EU and US markets have strict data protection and data security regulations in place that you will need to comply with.
In the EU, data protection is regulated by the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). In the US, data protection is regulated by HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). Where the GDPR regulates ALL the personal data of persons living in the EU, HIPAA has a much more narrow scope, zooming in on the PHI or Protected Health Information of patients.
We have written an elaborate blog post on the exact differences between GDPR and HIPAA if you require more information on this topic.
Read it here.
The importance of the IEC 62304 standard for SaMD development
The IEC 62304 standard is an international standard that defines a framework for software lifecycle processes, specifically for medical device software. The requirements are applied both for SaMDs and SiMDs.
As a SaMD manufacturer, you will need to comply with this standard in order to sell your solution in the EU, the US or both. As the software is an integral part of the SaMD, it’s best to start complying with the standard as soon as possible. A perfectly working solution means nothing if you’re not making sure it’s compliant. The standard also demands a QMS (see above) and recommends the ISO 13485 one.
Here at Extra Horizon, we have embedded quite the useful tool in the Extra Horizon medical Backend-as-a-Service platform, called the Software LifeCycle Tool. This tool enables you to implement software development processes to build IEC 62304 compliant documentation for your software code. The tool is integrated with Extra Horizon to streamline the compliance documentation generation for the configuration and facilitate your software release processes. All of this supports your compliance requirements for MDR in the EU market and FDA in the US market.
Clinical Evaluation of a SaMD
Clinical Evaluation is a dreaded step in the process of building and releasing a SaMD. Therefore, we have written a blog post specifically about the clinical evaluation phase for SaMDs in the EU, which you can read here.
We are also currently in the process of doing the same for clinical evaluation in FDA regulated markets, as this is a whole topic of its own, although similarities are present. So keep your eyes open for that blog post as well. If you want to receive updates like these directly in your inbox, you can always
subscribe to our newsletters as well.
How difficult is building an in-house SaMD solution?
Building a SaMD from scratch, in-house, is quite the challenge. This does not mean whatsoever that it’s not possible to do so, but it does require a highly competent and knowledgeable team, with lots of resources to support it.
How do we know? We have done it many times over together with our customers. When building a SaMD, there are many, many stakeholders and aspects to take into account. When first starting out, you will probably want to focus on attracting the right team members, getting funding, creating your first prototype and so on. In a later stage, you will need to perform clinical trials, expand your team, have some FTEs specifically for regulatory compliance, and so on.
We have written an interesting blog about the challenges of creating medical applications completely from scratch if you need some more in-depth information on this topic, read it here.
How our Medical Backend-as-a-Service platform, made for SaMD solutions, can help
Extra Horizon offers you a way to easily manage and scale your SaMD solution when going through the difficult process of ideating, prototyping, validating and launching your solution. All this while still enabling you to be easily compliant with all the regulatory requirements that pop up over time. It is, as you could say, the medical backend that grows as your company grows. So, let’s make your developers and regulatory colleagues happy by choosing the platform made for them, and start unburdening them as much as you can to focus more on your IP!
RECENT POSTS

FREE EBOOKS
GOT QUESTIONS?